Release 10.1.3.4
Part Number E12602-01
Contents
Previous
Next
| Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher Online Help Release 10.1.3.4 Part Number E12602-01 | Contents | Previous | Next |
This chapter covers the following topics:
BI Publisher relies on XML data to format and publish your reports. BI Publisher supports multiple methods for retrieving this data for your report. Moreover, you can combine data from different sources into a single report.
BI Publisher supports the following data model types:
Submit a SQL query against any of the transactional databases set up by your Administrator. BI Publisher also provides a Query Builder that enables you to build your SQL query graphically.
Use an RSS feed off the Web that returns XML.
Supply the Web service WSDL to BI Publisher and then define the parameters in BI Publisher to use a Web service to return data for your report.
The BI Publisher data engine enables you to rapidly generate any kind of XML data structure against any database in a scalable, efficient manner. The data template is the method by which you communicate your request for data to BI Publisher's data engine.
If you have integrated your BI Publisher installation with Oracle Business Intelligence Presentation Services, then you can use the data from an Oracle BI Answers request to create your report. For more information on this integration, see Integrating with Oracle Business Intelligence Presentation Services.
If you have integrated your BI Publisher installation with Oracle Discoverer, then you can use the data from an Oracle Discoverer worksheet to create your report. For more information on this integration, see Integration with Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer.
Use a pregenerated XML data file stored in a directory that has been set up by your Administrator.
Construct a multidimensional (MDX) query against an OLAP database that has been set up by your Administrator.
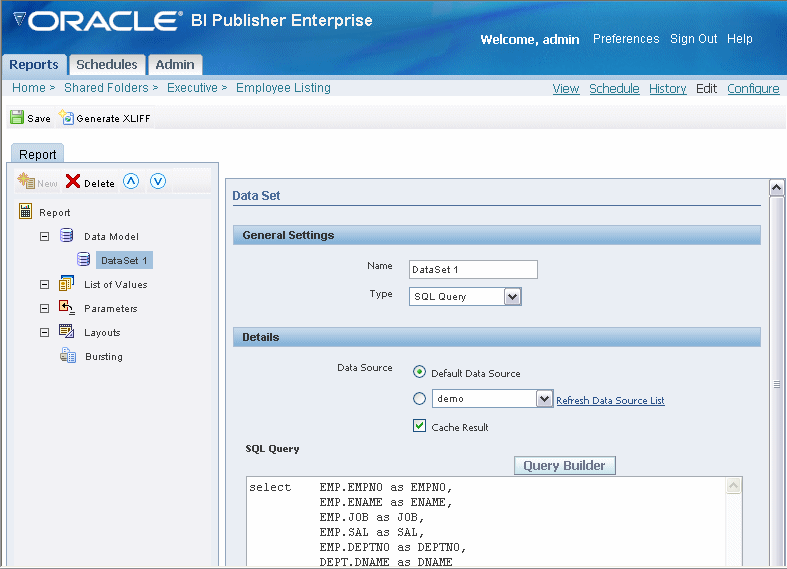
Select the Data Source for this data set. Select the Default Data Source (defined in the Report Properties) or select a new data source from the list.
Select the Cache Result box if you wish to cache the results of the query for your session.
By caching the results of the query, multiple templates can be applied to these results without requerying the data. This will enhance online performance. However, if the data is updated during the session, the user cannot view the new data via the View report page until the cache is cleared.
Note: You can control the cache expiration time and the cache size through the configuration settings. See Setting Server Configuration Options for more information.
Enter the SQL query or select Query Builder. See Using the Query Builder for information on the Query Builder utility.
Use the Query Builder to build SQL queries without coding. The Query Builder enables you to search and filter database objects, select objects and columns, create relationships between objects, and view formatted query results with minimal SQL knowledge.
The Query Builder page is divided into three sections:
Object Selection pane contains a list objects from which you can build queries. Only objects in the current schema display.
Design pane displays selected objects from the Object Selection pane.
Output pane allows you to create conditions, view the generated SQL, or view query results.
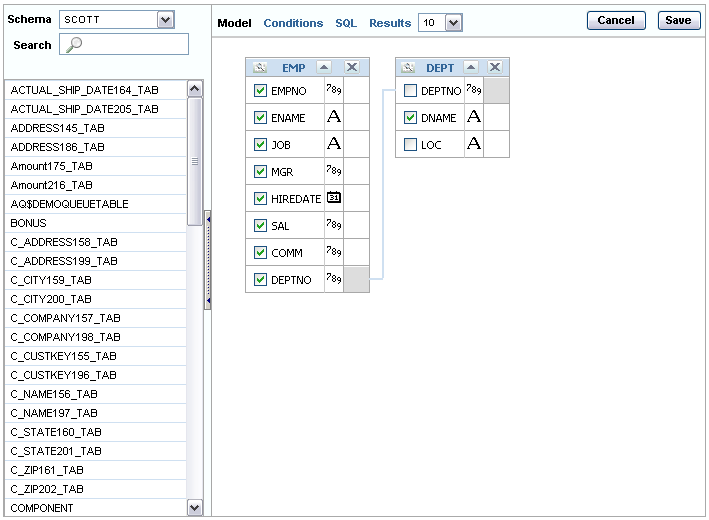
To build a query, perform the following steps:
Select objects from the Object Selection pane.
Add objects to the Design pane and select columns.
Optional: Establish relationships between objects.
Optional: Create query conditions.
Execute the query and view results.
In the Object Selection pane you can select a schema and search and filter objects.
To hide the Object Selection pane, select the control bar located between it and the Design pane. Select it again to unhide it.
The Schema list contains all the available schemas in the data source. Note that you may not have access to all that are listed.
Use the Search field to enter a search string. Note that if more than 100 tables are present in the data source, you must use the Search feature to locate and select the desired objects.
The Object Selection pane lists the tables, views, and materialized views from the selected schema (for Oracle databases, synonyms are also listed). Select the object from the list and it displays on the Design pane. Use the Design pane to identify how the selected objects will be used in the query.
Columns of all types display as objects in the Design pane. Note the following column restrictions:
Each can select no more than 60 columns for each query.
Only the following column types are selectable:
VARCHAR2, CHAR
NUMBER
DATE, TIMESTAMP
BLOB
Note: The BLOB must be XML or an image. When you execute the query in the Query Builder, the BLOB will not display in the Results pane, however, the query will be constructed correctly when saved to the Report Editor.
XMLType
Note: When you execute the query in the Query Builder, the XMLType will display as null. When you save the query to the Report Builder, you must add the function (such as getClobval()) to extract the XML from the type.
Select an object.
The selected object displays in the Design pane. An icon representing the datatype displays next to each column name.
Select the check box for each column to include in your query.
When you select a column, it appears on the Conditions tab. Note that the Show check box on the Conditions tab controls whether a column is included in query results. Be default, this check box is selected.
To select the first twenty columns, click the small icon in the upper left corner of the object and then select Check All.
To execute the query and view results, select Results.
Tip: You can also execute a query using the key strokes CTRL + ENTER.
As you select objects, you can resize the Design and Results panes by selecting and dragging the gray horizontal rule dividing the page.
To remove an object, select the Remove icon in the upper right corner of the object.
To temporarily hide the columns within an object, click the Show/Hide Columns icon.
Conditions enable you to filter and identify the data you want to work with. As you select columns within an object, you can specify conditions on the Conditions tab. You can use these attributes to modify the column alias, apply column conditions, sort columns, or apply functions.
When you select a column to include in your query, it appears as a separate row in the Output pane. The following table describes the attributes available on the Conditions tab:
| Condition Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Up and Down Arrows | Controls the display order of the columns in the resulting query. |
| Column | Displays the column name. |
| Alias | Specify an optional column alias. An alias is an alternative column name. Aliases are used to make a column name more descriptive, to shorten the column name, or prevent possible ambiguous references. |
| Condition | The condition modifies the query's WHERE clause. When specifying a column condition, you must include the appropriate operator and operand. All standard SQL conditions are supported. For example: >=10 ='VA' IN (SELECT dept_no FROM dept) BETWEEN SYSDATE AND SYSDATE + 15 |
| Sort Type | Select ASC (Ascending) or DESC (Descending). |
| Sort Order | Enter a number (1, 2, 3, and so on) to specify the order in which selected columns should display. |
| Show | Select this check box to include the column in your query results. You do not need to select Show if you need to add a column to the query for filtering only. For example, suppose you wish to create following query: To create this query in Query Builder:
|
| Function | Available argument functions include:
|
| Group By | Specify columns to be used for grouping when an aggregate function is used. Only applicable for columns included in output. |
| Delete | Deselect the column, excluding it from the query. |
As you select columns and define conditions, Query Builder writes the SQL for you.
To view the underlying SQL, click the SQL tab
You can create relationships between objects by creating a join. A join identifies a relationship between two or more tables, views, or materialized views.
When you write a join query, you specify a condition that conveys a relationship between two objects. This condition is called a join condition. A join condition determines how the rows from one object will combine with the rows from another object.
Query Builder supports inner, outer, left, and right joins. An inner join (also called a simple join) returns the rows that satisfy the join condition. An outer join extends the result of a simple join. An outer join returns all rows that satisfy the join condition and returns some or all of those rows from one table for which no rows from the other satisfy the join condition.
Note: See Oracle Database SQL Reference for information about join conditions.
Create a join manually by selecting the Join column in the Design pane.
From the Object Selection pane, select the objects you want to join.
Identify the columns you want to join.
You create a join by selecting the Join column adjacent to the column name. The Join column displays to the right of the datatype. When your cursor is in the appropriate position, the following help tip displays:
Click here to select column for join
Select the appropriate Join column for the first object.
When selected, the Join column is darkened. To deselect a Join column, simply select it again or press ESC.
Select the appropriate Join column for the second object.
When joined, line connects the two columns. An example is shown in the following figure:
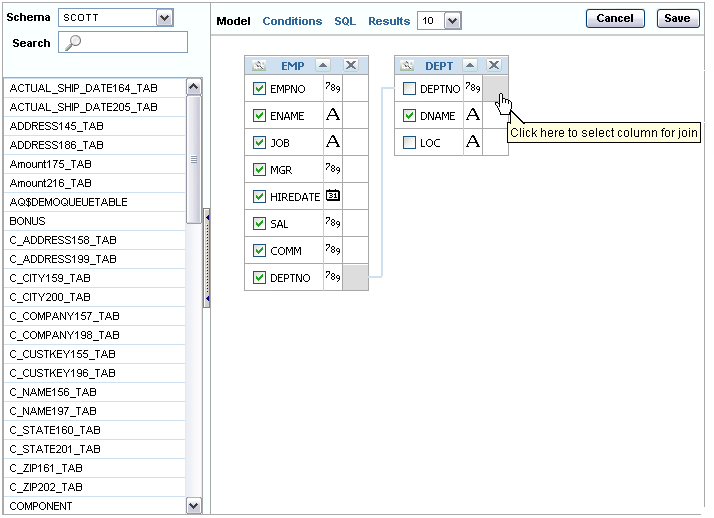
Select the columns to be included in your query. You can view the SQL statement resulting from the join by positioning the cursor over the join line.
Click Results to execute the query.
Once you have built the query and executed it, select the Save button to return to the Report Editor. The query will appear in the SQL Query box.
Once you have saved the query from the Query Builder to the Report Editor, simply select Query Builder again to edit the query. The Query Builder will parse the query and present it for modification in the Query Builder interface.
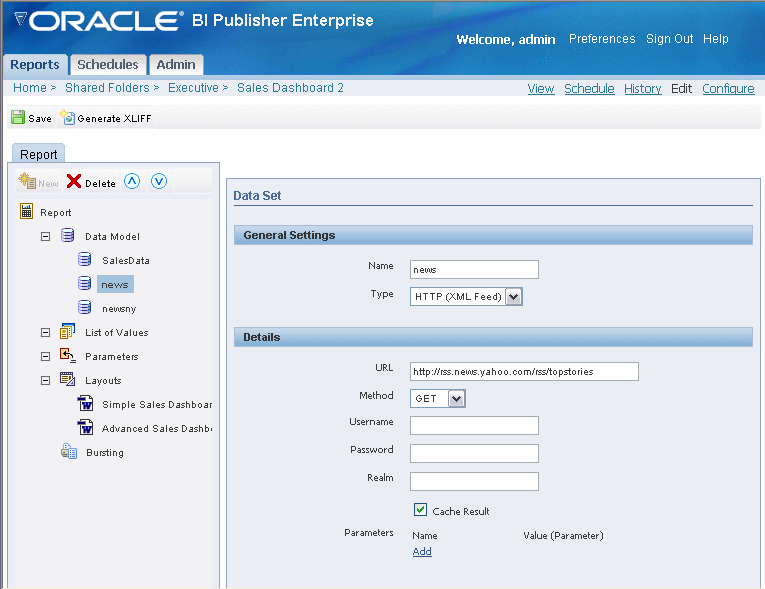
Using the HTTP data source type you can create reports from RSS feeds over the Web.
Note that if you want to include parameters for an HTTP (XML feed), you must define the parameters first, so that they are available for selection when setting up the data source. See Adding Lists of Values and Parameters.
Enter the URL for the XML feed.
Select the Method: Get or Post.
Enter the Username, Password, and Realm for the URL, if required.
Select the Cache Result box if you wish to cache the results of the query for your session.
By caching the results of the query, multiple templates can be applied to these results without requerying the data. This will enhance online performance. However, if the data is updated during the session, the user cannot view the new data via the View report page until the cache is cleared.
Note: You can control the cache expiration time and the cache size through the configuration settings. See Setting Server Configuration Options for more information.
To add a parameter, select the Add link. Enter the Name and select the Value. The Value list is populated by the parameter Identifiers defined in the Parameters section. See Adding Parameters and Lists of Values.
BI Publisher supports document/literal Web service data sources that return the following data types:
string
boolean
dateTime
decimal
integer
Tip: If the WSDL URL is outside of your company firewall you must start the BI Publisher sever using proxy parameters.
BI Publisher supports Web services that return both simple data types and complex data types. You must make the distinction between simple and complex when you define the Web service data model. See Adding a Simple Web Service and Adding a Complex Web Service for descriptions of setting up each type.
Note that if you want to include parameters for the Web service method, you must define the parameters first, so that they are available for selection when setting up the data source. See Adding Parameters and Lists of Values.
Multiple parameters are supported. Ensure the method name is correct and the order of the parameters matches the order in the method. If you want to call a method in your Web service that accepts two parameters, you must map two parameters defined in the report to those two. Note that only parameters of simple type are supported, for example, string and integer.
Enter the WSDL URL and the Web Service Method.
Important: Only document/literal Web services are supported.
To specify a parameter, select the Add link. Select the parameter from the list.
Note: The parameters must already be set up in the Parameters section of the report definition See Adding Parameters and Lists of Values.
This example shows how to add a Web service to BI Publisher as a data source. The Web service returns stock quote information. The Web service will pass one parameter: the quote symbol for a stock.
The WSDL URL is:
http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx?WSDLIf you are not already familiar with the available methods and parameters in the Web service that you want to call, you can open the URL in a browser to view them. This Web service includes a method called GetQuote. It takes one parameter, which is the stock quote symbol.
To add the Web service as a data source:
Enter the Data Set information:
Enter a Name for the Data Set and select Web Service as the Type.
Select False for Complex Type.
Enter the WSDL URL: http://www.webservicex.net/stockquote.asmx?WSDL
Enter the Method: GetQuote
If desired, enter a Time Out period in seconds. If the BI Publisher server cannot establish a connection to the Web service, the connection attempt will time out after the specified time out period has elapsed.
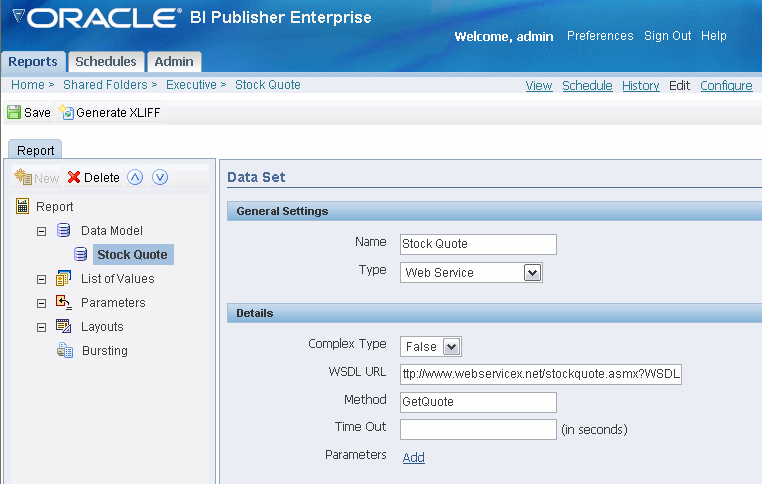
Define the parameter to make it available to the Web service data set.
Select Parameters on the Report definition pane and click New to create a new parameter. Enter the following:
Identifier - enter an internal identifier for the parameter.
Data Type - String
Default Value - if desired, enter a default for the parameter.
Parameter Type - Text
Display label - enter the label you want displayed for your parameter.
Text Field Size - enter the size for the text entry field in characters.
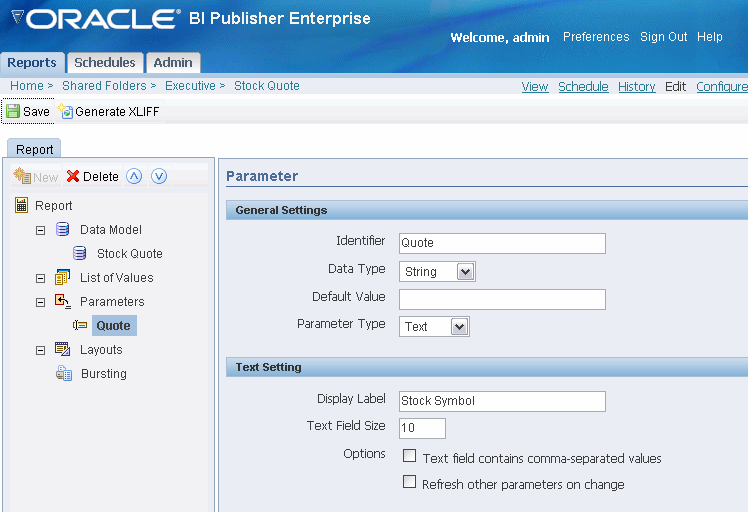
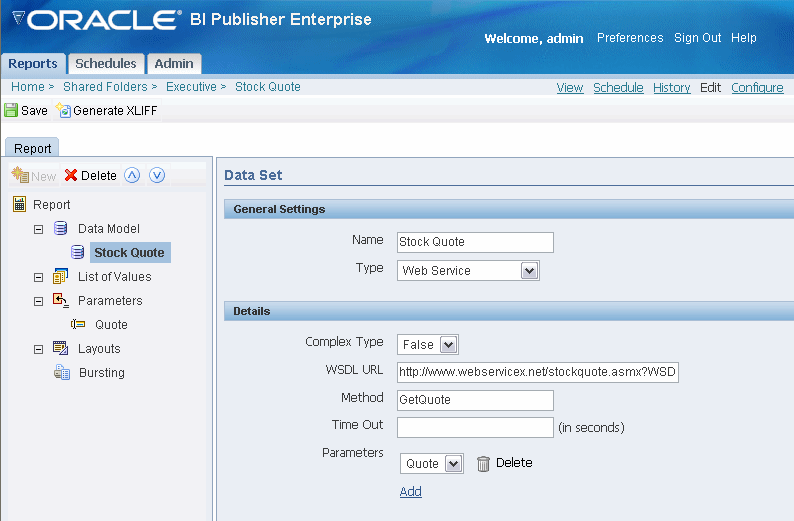
Return to your Web service data set and add the parameter.
In the Details section under Parameters, Select Add. The Quote parameter you specified is now available from the list.
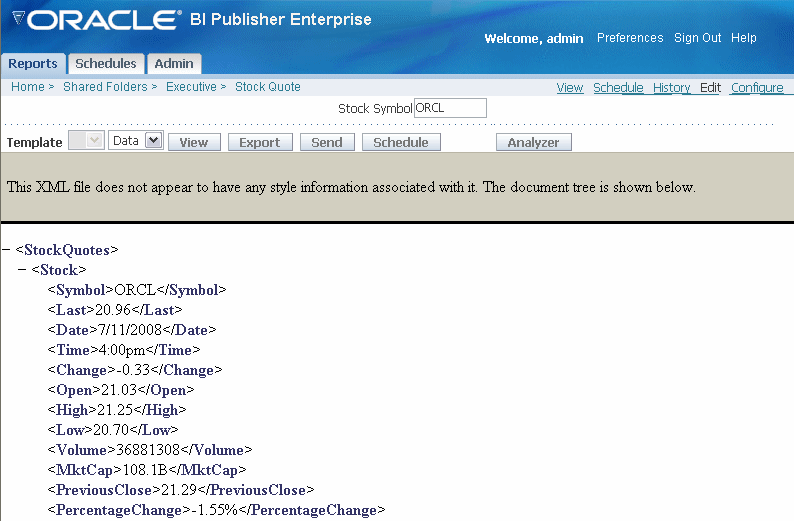
To view the results XML, select View. Enter a valid value for your Stock Quote parameter and select View again.
You can also add a complex Web service to BI Publisher as a data source. A complex Web service returns complex data types rather than simple string XML.
To use a complex Web service as a data source, select Complex Type equal True, then enter the WSDL URL. After loading and analyzing the WSDL URL, the Report Editor screen will display the available Web services and operations. For each selected operation, the Report Editor will display the structure of the input parameters. By choosing "show optional parameters", you can see all optional parameters as well.
If you are not already familiar with the available methods and parameters in the Web service that you want to call, you can open the URL in a browser to view them.
To add a complex Web service as a data source:
Enter the Data Set information:
Enter a Name for the Data Set and select Web Service as the Type.
Select True for Complex Type.
Select a security header:
Disabled - does not insert a security header.
2002 - enables the "WS-Security" Username Token with the 2002 namespace: http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-secext-1.0.xsd
2004 - enables the "WS-Security" Username Token with the 2004 namespace:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-username-token-profile-1.0#PasswordText
Username and Password - enter the username and password for the Web service, if required.
If desired, enter a Time Out period in seconds. If the BI Publisher server cannot establish a connection to the Web service, the connection attempt will time out after the specified time out period has elapsed.
Enter a WSDL URL. When you enter the WSDL, the Web Service list will populate with the available Web services from the WSDL.
Choose a Web Service from the list. When you choose a Web service from the list, the Method list will populate with the available methods.
Select the Method. When you select the method, the Parameters will display. If you wish to see optional parameters as well, select Show Optional Parameters.
Define the parameter to make it available to the Web service data set.
Select Parameters on the Report definition pane and click New to create a new parameter. Enter the following:
Identifier - enter an internal identifier for the parameter.
Data Type - String
Default Value - if desired, enter a default for the parameter.
Parameter Type - Text
Display label - enter the label you want displayed for your parameter.
Text Field Size - enter the size for the text entry field in characters.
Return to your Web service data set and add the parameter.
In the entry field for the Parameter, enter the following syntax: ${Parameter_Identifier} where Parameter_Identifier is the value you entered for Identifier when you defined the parameter to BI Publisher.
To view the results XML, select View. Enter a value for your parameter and select View again.
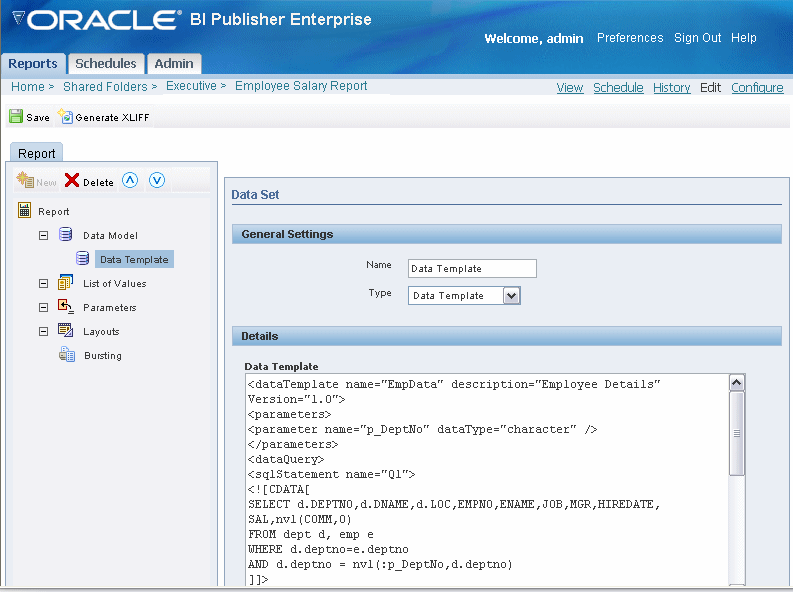
Use the BI Publisher data template to create more complex SQL queries. See Building a Data Template for features and usage. Please note that lexical parameters are only supported when executing a query against an Oracle E-Business Suite instance.
Enter the data template code directly in the Data Template text box, or copy and paste the data template from another text source.
Important: If copying the data template, the entry in the text box must begin with the <dataTemplate> element. Do not include the XML declaration.
If you have enabled integration with Oracle Business Intelligence Presentation Services, then you can access the BI catalog to select an Oracle BI Answers request as a data source. Oracle BI Answers is an ad hoc query building tool included in the Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition. For more information on building Oracle BI Answers see the Oracle Business Intelligence Answers, Delivers, and Interactive Dashboards User Guide.
Choose Oracle BI Answers as the data set Type.
Note: BI Publisher does not support lists of values and parameters for the Oracle BI Answers request data set type.
Select the browse icon to connect to the Oracle BI Answers catalog. This action displays the folders you have access to on the Oracle BI Presentation Services server.
Note: You must set up integration with Oracle BI Presentation Services to enable Oracle BI Answers as a data set Type. See
Select the Answers request you wish to use as the data set for your report.
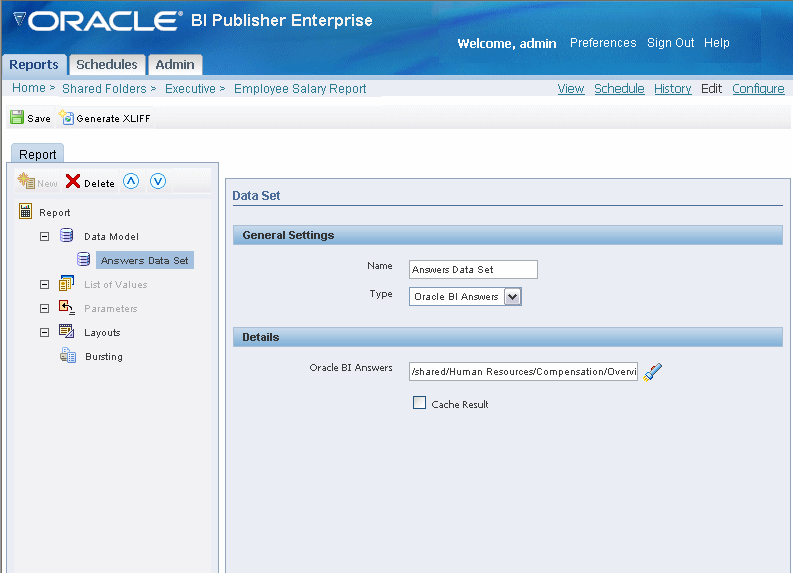
Select the Cache Result box if you wish to cache the results of the query for your session.
By caching the results of the query, multiple templates can be applied to these results without requerying the data. This will enhance online performance. However, if the data is updated during the session, the user cannot view the new data via the View report page until the cache is cleared.
Note: You can control the cache expiration time and the cache size through the configuration settings. See Setting Server Configuration Options for more information.
For integration with BI Discoverer, you must configure the data source through the Oracle BI Discoverer tab on the Integration page from the Oracle BI Publisher Admin page. See Setting Up Integration with Oracle BI Discoverer for prerequisites, limitations, and setup details.
Note: A data model can include only one data set based on a Discoverer Worksheet.
Select Oracle BI Discoverer from the Data Set Type list. This will enable the appropriate Details region for the Discoverer data source.
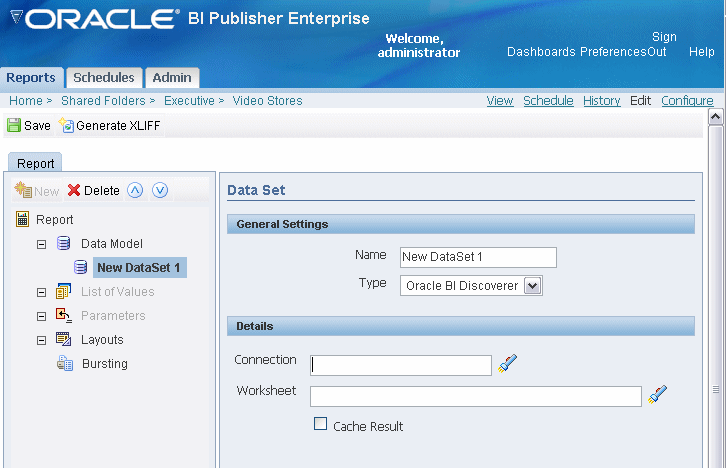
Enter the Details:
Connection - click the search icon to launch the list of available Discoverer connections. Navigate to and select the Discoverer connection that owns the worksheet you want to use in your report.
Worksheet - click the search icon to launch the list of available workbooks. Navigate to and select the workbook and then the worksheet you want to base your report on. When you make your selection, BI Publisher inserts the fully qualified path to the worksheet in the field.
Note: Regardless of whether the Discoverer worksheet is a tabular or crosstab layout, the Discoverer Web service will return the data to Oracle BI Publisher as flat tabular data. This is by design so that you can take full advantage of the layout capabilities in BI Publisher. You can layout this data as a crosstab in BI Publisher.
Save your report.
Click View to ensure that the Discoverer Worksheet you selected returns data to the report. If your worksheet contains parameters, you may need to select values other than the default and click View again to enable the worksheet to return data.
When you set up data sources (see Setting Up Data Sources) you can define a file directory as a data source. You can then place xml documents in the file directory to access directly as data sources for your reports.
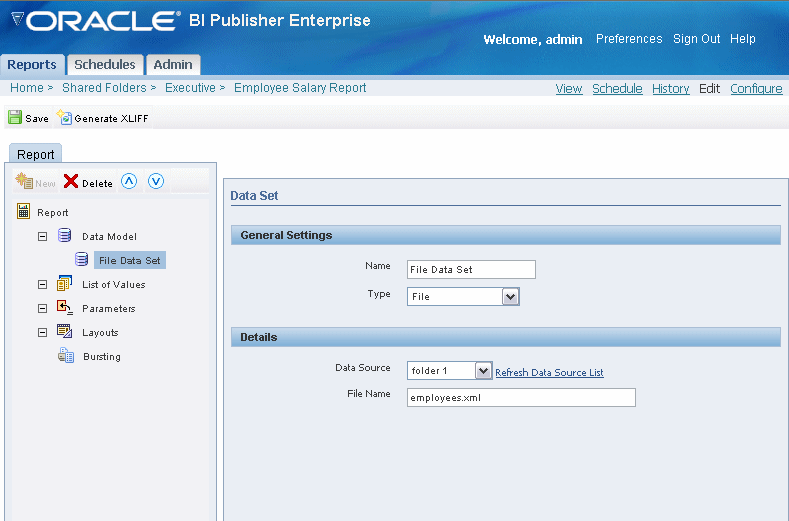
Choose File as the data set Type.
Choose the appropriate file directory as the Data Source.
Enter the File Name of the XML document to use as the report data set. If the file resides in a subdirectory, include the path.
BI Publisher supports Multidimensional Expressions (MDX) queries against your OLAP data sources. MDX lets you query multidimensional objects, such as cubes, and return multidimensional cellsets that contain the cube's data. See your OLAP database documentation for information on the MDX syntax and functions it supports.
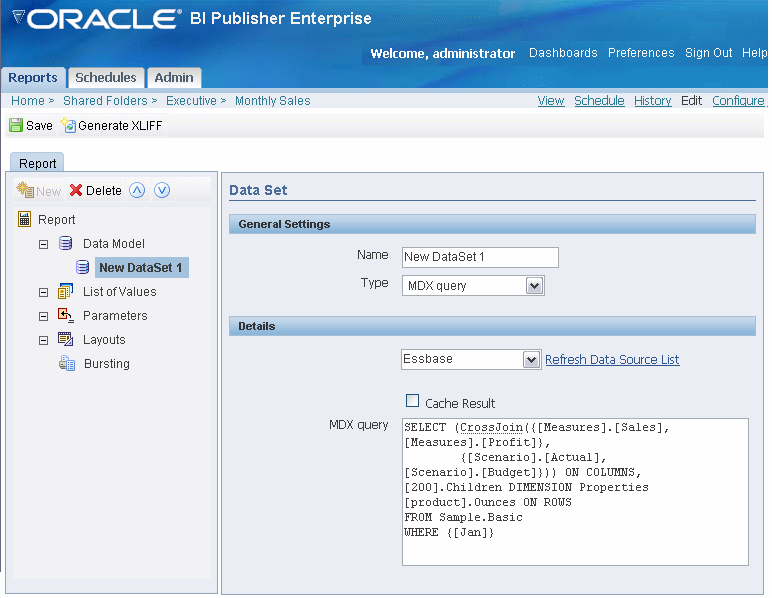
Select the Data Source for this data set. Select the Default Data Source (defined in the Report Properties) or select a new data source from the list. Only data sources defined as OLAP connections will display in the list.
Select the Cache Result box if you wish to cache the results of the query for your session.
By caching the results of the query, multiple templates can be applied to these results without requerying the data. This will enhance online performance. However, if the data is updated during the session, the user cannot view the new data via the View report page until the cache is cleared.
Note: You can control the cache expiration time and the cache size through the configuration settings. See Setting Server Configuration Options for more information.
Enter the MDX query by direct entry or by copying and pasting from a third-party MDX editor.
Click Save.
Test your query by selecting the View link. This will launch the Report Viewer page. Select View again to display the data set returned by your query.
Select the Edit link to return to the Report Editor.
![]()
Copyright © 2005, 2008, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.